Canes Venatici: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:375px-Canes Venatici IAU.svg.png|thumb|Canes Venatici]] | |||
[[Canes Venatici]] is one of the 88 official modern constellations. It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighboring constellation. | [[Canes Venatici]] is one of the 88 official modern constellations. It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighboring constellation. | ||
The stars of Canes Venatici are not bright. In classical times, they were included byPtolemy within the constellation Ursa Major in his star catalogue. α CVn was Ptolemy's "28th of Ursa Major", and β CVn was his "29th of Ursa Major". In medieval times, the identification of these stars with the dogs of Boötes arose through a mistranslation. Some of Boötes's stars were traditionally described as representing the club (Greek, Κολλοροβος) of Boötes. | The stars of Canes Venatici are not bright. In classical times, they were included byPtolemy within the constellation Ursa Major in his star catalogue. α CVn was Ptolemy's "28th of Ursa Major", and β CVn was his "29th of Ursa Major". In medieval times, the identification of these stars with the dogs of Boötes arose through a mistranslation. Some of Boötes's stars were traditionally described as representing the club (Greek, Κολλοροβος) of Boötes. | ||
[[Canes Venatici]] is bordered by Ursa Major to the north and west, Coma Berenices to the south, and Boötes to the east. The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1922, is 'CVn'. | [[Canes Venatici]] is bordered by Ursa Major to the north and west, Coma Berenices to the south, and Boötes to the east. The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1922, is 'CVn'.The official constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined by a polygon of 14 sides. In theequatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 12h 06.2m and 14h 07.3m, while the declination coordinates are between +27.84° and +52.36°. Covering 465 square degrees, it ranks 38th of the 88 constellations in size. | ||
Canes Venatici contains five Messier objects, including four galaxies. One of the more significant galaxies in Canes Venatici is the Whirlpool Galaxy ([[Messier 51]], NGC 5194) and NGC 5195, a small barred spiral galaxy that is seen face on. This was the first galaxy recognised as having a spiral structure, this structure being first observed by Lord Rosse in 1845.<ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canes_Venatici Canes Venatici]</ref> | Canes Venatici contains five Messier objects, including four galaxies. One of the more significant galaxies in Canes Venatici is the Whirlpool Galaxy ([[Messier 51]], NGC 5194) and NGC 5195, a small barred spiral galaxy that is seen face on. This was the first galaxy recognised as having a spiral structure, this structure being first observed by Lord Rosse in 1845.<ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canes_Venatici Canes Venatici]</ref> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
==HGS Session References== | ==HGS Session References== | ||
HGS Sessions - Clearing [[Hyperspace Phantom Matrix]] - 3/12/2015 <ref>[ | HGS Sessions - Clearing [[Hyperspace Phantom Matrix]] - 3/12/2015 <ref>HGS Session</ref>HGS Sessions - Clearing [[Tara, Gaia, Cradle of Lyra]]- 3/12/2015 <ref> HGS Session</ref>HGS Sessions - Clearing [[San Francisco Golden Gate Bridge, 55 Reversal Grid]] - 3/31/2015 <ref>HGS Session</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:08, 2 April 2015
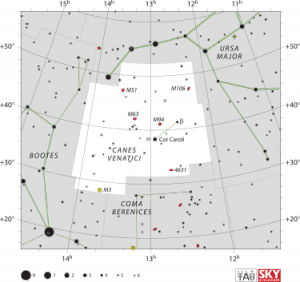
Canes Venatici is one of the 88 official modern constellations. It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighboring constellation.
The stars of Canes Venatici are not bright. In classical times, they were included byPtolemy within the constellation Ursa Major in his star catalogue. α CVn was Ptolemy's "28th of Ursa Major", and β CVn was his "29th of Ursa Major". In medieval times, the identification of these stars with the dogs of Boötes arose through a mistranslation. Some of Boötes's stars were traditionally described as representing the club (Greek, Κολλοροβος) of Boötes.
Canes Venatici is bordered by Ursa Major to the north and west, Coma Berenices to the south, and Boötes to the east. The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1922, is 'CVn'.The official constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined by a polygon of 14 sides. In theequatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 12h 06.2m and 14h 07.3m, while the declination coordinates are between +27.84° and +52.36°. Covering 465 square degrees, it ranks 38th of the 88 constellations in size.
Canes Venatici contains five Messier objects, including four galaxies. One of the more significant galaxies in Canes Venatici is the Whirlpool Galaxy (Messier 51, NGC 5194) and NGC 5195, a small barred spiral galaxy that is seen face on. This was the first galaxy recognised as having a spiral structure, this structure being first observed by Lord Rosse in 1845.[1]
Supervoid
The Giant Void, an extremely large void (part of the universe containing very few galaxies) is within the vicinity of this constellation. It may be possibly the largest void ever discovered, sightly larger than the Eridanus Supervoid and 1,200 times the volume of expected typical voids. It was discovered in 1988 in a deep-sky survey.
HGS Session References
HGS Sessions - Clearing Hyperspace Phantom Matrix - 3/12/2015 [2]HGS Sessions - Clearing Tara, Gaia, Cradle of Lyra- 3/12/2015 [3]HGS Sessions - Clearing San Francisco Golden Gate Bridge, 55 Reversal Grid - 3/31/2015 [4]
References
- ↑ Canes Venatici
- ↑ HGS Session
- ↑ HGS Session
- ↑ HGS Session
Found in HGS Manual on Page 108
Found in HGS Manual on Page 115

