Indus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:375px-Indus IAU.svg (1).png|thumb|Indus]] | |||
Indus is a constellation in the southern sky. Created in the late sixteenth century, it represents an Indian, a word that could refer at the time to any native of Asia or the Americas. | Indus is a constellation in the southern sky. Created in the late sixteenth century, it represents an Indian, a word that could refer at the time to any native of Asia or the Americas. | ||
The constellation was one of twelve created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyserand Frederick de Houtman[2] and it first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius with Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was inJohann Bayer's Uranometria of 1603. Plancius portrayed the figure as a nude male with arrows in both hands but no bow. | The constellation was one of twelve created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyserand Frederick de Houtman[2] and it first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius with Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was inJohann Bayer's Uranometria of 1603. Plancius portrayed the figure as a nude male with arrows in both hands but no bow. | ||
<ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indus_%28constellation%29 Indus]</ref> | |||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
The word Indus comes from the name of India. It originally derived from the river Indus that originates in Tibet and flows through Pakistan into the Arabian Sea. The ancient Greeks called this river Indos. Related words are: Hindu, indigo (Greek indikon, Latin indicum, 'from India', a blue dye from India, derived from the plantIndigofera), indium (the element is named after indigo), sandia (a watermelon), sendal (a fabric, from Greeksindon, fine linen), sindon (fine linen fabric).<ref> | The word Indus comes from the name of India. It originally derived from the river Indus that originates in Tibet and flows through Pakistan into the Arabian Sea. The ancient Greeks called this river Indos. Related words are: Hindu, indigo (Greek indikon, Latin indicum, 'from India', a blue dye from India, derived from the plantIndigofera), indium (the element is named after indigo), sandia (a watermelon), sendal (a fabric, from Greeksindon, fine linen), sindon (fine linen fabric).<ref>[http://www.constellationsofwords.com/Constellations/Indus.htm Constellation of Words]</ref> | ||
==HGS Session References== | ==HGS Session References== | ||
Latest revision as of 00:45, 17 March 2015
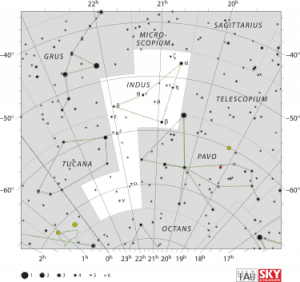
Indus is a constellation in the southern sky. Created in the late sixteenth century, it represents an Indian, a word that could refer at the time to any native of Asia or the Americas. The constellation was one of twelve created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyserand Frederick de Houtman[2] and it first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius with Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was inJohann Bayer's Uranometria of 1603. Plancius portrayed the figure as a nude male with arrows in both hands but no bow. [1]
Etymology
The word Indus comes from the name of India. It originally derived from the river Indus that originates in Tibet and flows through Pakistan into the Arabian Sea. The ancient Greeks called this river Indos. Related words are: Hindu, indigo (Greek indikon, Latin indicum, 'from India', a blue dye from India, derived from the plantIndigofera), indium (the element is named after indigo), sandia (a watermelon), sendal (a fabric, from Greeksindon, fine linen), sindon (fine linen fabric).[2]
HGS Session References
HGS Sessions - Clearing Hyperspace Phantom Matrix - 3/12/2015 [3]
References
Found in HGS Manual on Page 108
Found in HGS Manual on Page 115

