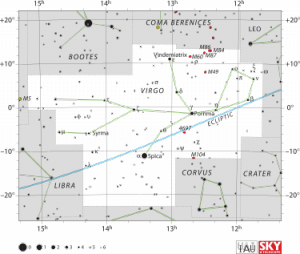
Virgo
Virgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for virgin, and its symbol is ♍. Lying between Leo to the west and Libra to the east, it is the second largest constellation in the sky (after Hydra). It can be easily found through its brightest star, Spica.
The bright Spica makes it easy to locate Virgo, as it can be found by following the curve of the Big Dipper/Plough to Arcturus in Boötes and continuing from there in the same curve ("follow the arc to Arcturus and speed on to Spica").
Due to the effects of precession, the First Point of Libra, (also known as the autumn equinox point) lies within the boundaries of Virgo very close to β Virginis. This is one of the two points in the sky where the celestial equatorcrosses the ecliptic (the other being the First Point of Aries, now in the constellation of Pisces.) This point will pass into the neighbouring constellation of Leo around the year 2440.There are 35 verified exoplanets orbiting 29 stars in Virgo, including PSR B1257+12 (three planets), 70 Virginis (one planet), Chi Virginis (one planet), 61 Virginis (three planets), NY Virginis (two planets), and 59 Virginis (one planet).Because of the presence of a galaxy cluster (consequently called the Virgo cluster) within its borders 5° to 12° west of ε Vir (Vindemiatrix), this constellation is especially rich in galaxies.
Some examples are Messier 49 (elliptical), Messier 58 (spiral), Messier 59 (elliptical), Messier 60 (elliptical), Messier 61 (spiral), Messier 84 (lenticular), Messier 86 (lenticular), Messier 87 (elliptical and a famous radio source), Messier 89 (elliptical) and Messier 90 (spiral). A noted galaxy that is not part of the cluster is the Sombrero Galaxy (M104), an unusual spiral galaxy. It is located about 10° due west of Spica.
Mythology
According to the Babylonian Mul.Apin, which dates from 1000–686 BCE, this constellation was known as "The Furrow", representing the goddess Shala's ear of grain or corn. One star in this constellation, Spica, retains this tradition as it is Latin for "ear of grain", one of the major products of the Mesopotamian furrow. The constellation was also known as AB.SIN and absinnu. For this reason the constellation became associated with fertility.[6] According to Gavin White the figure of Virgo corresponds to two Babylonian constellations - the 'Furrow' in the eastern sector of Virgo and the 'Frond of Erua' in the western sector. The Frond of Erua was depicted as a goddess holding a palm-frond - a motif that still occasionally appears in much later depictions of Virgo.
The Greeks and Romans associated Virgo with their goddess of wheat/agriculture, Demeter-Ceres who is the mother of Persephone-Proserpina. Alternatively, she was sometimes identified as the virgin goddess Iustitia or Astraea, holding the scales of justice in her hand as the constellation Libra. Another myth identifies Virgo as Erigone, the daughter of Icarius of Athens. Icarius, who had been favoured by Dionysus, was killed by his shepherds while they were intoxicated and Erigone hanged herself in grief; Dionysus placed the father and daughter in the stars as Boötes and Virgo respectively. In the Middle Ages, Virgo was sometimes associated with the Blessed Virgin Mary.
HGS Session References
HGS Sessions - Clearing Hyperspace Phantom Matrix - 3/12/2015 [1]
References
Found in HGS Manual on Page 108
Found in HGS Manual on Page 115